Mirrored Gardens geological strata: the shop 2018 edition No.3:
Michele Ciacciofera:
The Translucent Skin of The Present
Acting with materials, pictograms, colors, signs and texture, this body of works organically want to take anyone lives and comes at Mirrored Gardens through a dimension in which my art practice, in a variety of materials including different ceramic techniques, mythological forms, a collection of visionary books, textiles etc. offers a vision of an unlimited life with no beginning and mostly no end as a flowing liquid.
Drawing from both abstract and figurative forms, craft tradition and writings, combined with references from literature, anthropology, archaeology and history, this installation intends to push these practices into new directions, bringing them together to create an original and divergent visual language his own, in a constant dialogue with the natural surroundings and the local culture through a pluralism of traditions where no dominant experience, skill or culture persists.
These works are mainly characterized by a sense of exploration of the human forms and his original practices as writing, drawing, praying. Exploring the reality in all its vastness and crossing ages and cultures from the Neolithic, as a fundamental starting reference for human creativity, to now these materials, figures and forms want to resist easy categorization, allowing for different layers of readings and experiences.
My practice compares to that of an archaeologist and anthropologist as an art of excavation impregnated by mythology, popular legends and real experiences through the most important historical venues in the Mediterranean culture as the two islands of Sardinia and Sicily are.
This research forms part of my personal sociological and anthropological education, it is inscribed in my Mediterranean DNA, as a man born in Sardinia and raised in Sicily, among the nuraghi, the Greek temples and the fragments of antiquities that sometimes still emerge from the ground as flowers do.
(Written in Mirriored Gardens by Michele Ciacciofera)
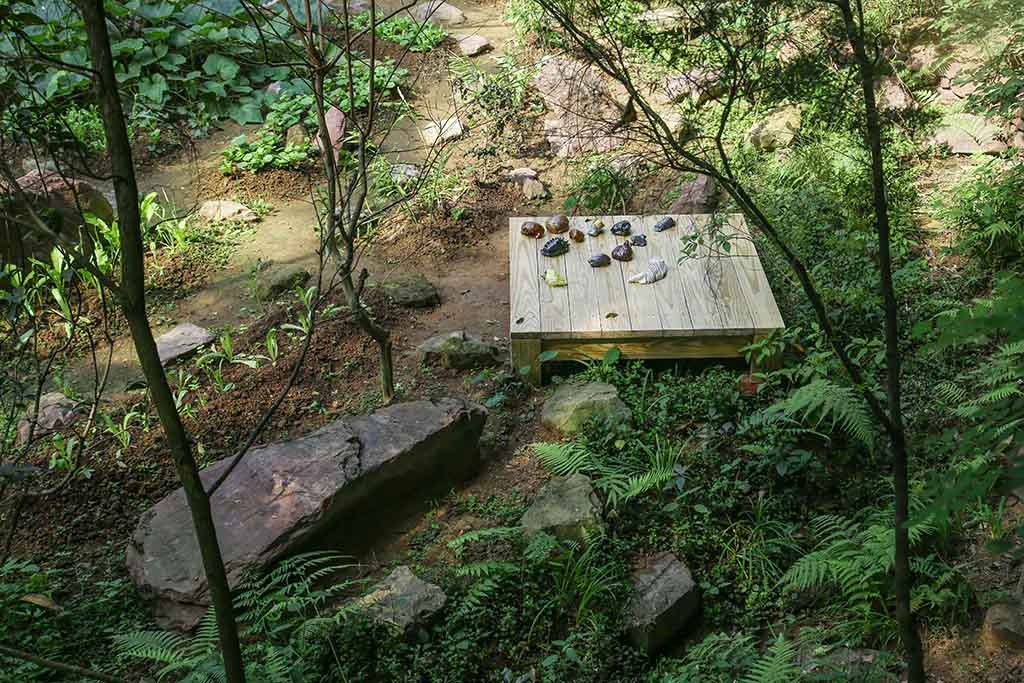

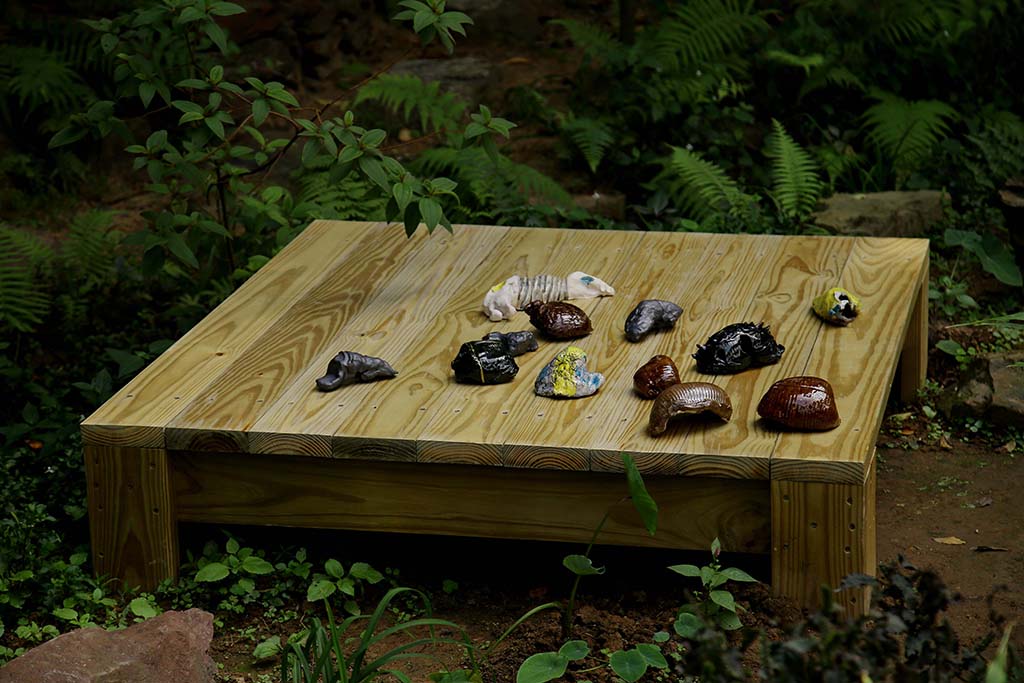
Fossil / Trilobite
“Collecting them is a kind of mania – they are beings/objects with what I believe to be a perfect shape, but science is not yet able to tell us everything about them, making them mysterious and fascinating.”
“They act as an archive because they encompass memory, while on the other hand these fossils inspired me to start reconstructing forms that are also the result of the psychological processing of reality.”
——Michele Ciacciofera
A Fossil is any preserved remains, impression, or traces of any once-living thing from a past geological age. These ancient remains turned into existences appearing to rocks after a long and complicated transformation (including permineralization, casts and molds, authigenic mineralization, replacement and recrystallization, adpression, carbonization, and bioimmuration).
Trilobites are a group of extinct marine arthropods. The earliest fossil record of trilobite dates back to the Early Cambrian period (521 million years ago). Trilobites disappeared in the mass extinction at the end of the Permian (252 million years ago).
“Trilobite” means “three lobed,” which is in reference to trilobites’ body plan that divides into three body parts both horizontally and vertically.
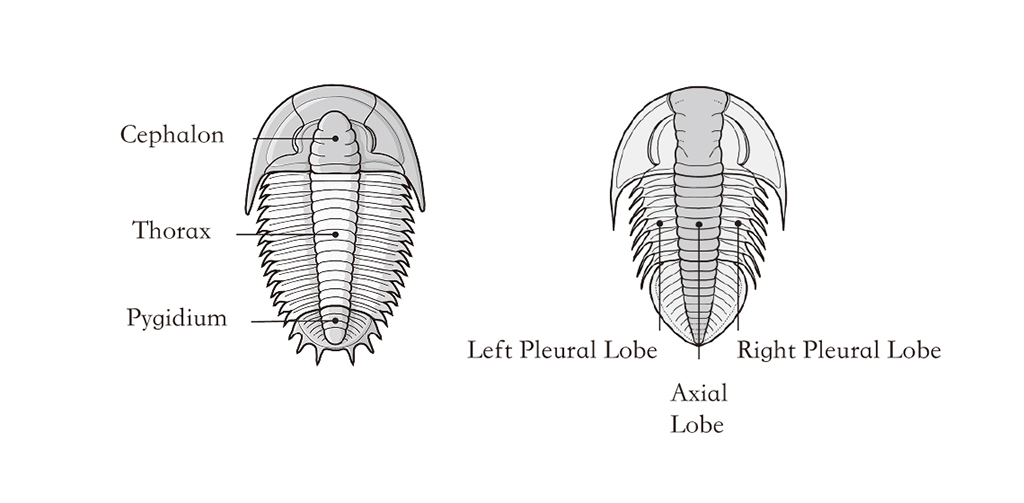
Fossils of trilobite scattered all over the planet, with a wide range of known species of more than 17000.
A trilobite casted off its exoskeleton for several times through its life. The reason of which fossils of trilobites are worldwide preserved is that the mineral content, high in calcite (CaCO3), in their exoskeleton makes them difficult to be decomposed. The quantity and geological distribution of trilobite fossils offers a strong evidence for the Continental Drift.
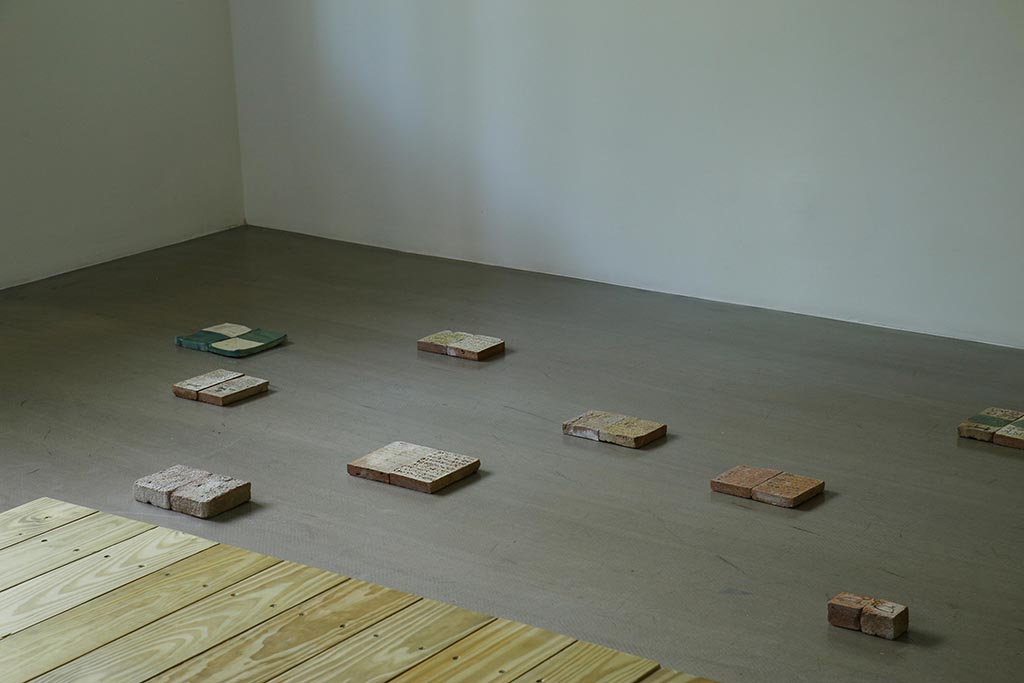


Writing / Sign
“My interest in memory is born out of several considerations, but first and foremost out of the awareness that our identity is the history of the generations that preceded us, written and told in and by the system of tangible and imaginary symbols that represent it.”
“In both Sardinia and Sicily, several islands exist alongside one another within the islands themselves, and all of this is very fragile. By this I don’t mean it is all disappearing, but I think that today the language of art can seek to recover linguistic values. Deep down, language are symbols, pillars of identity, which are threatened with extinction, but which can be relaunched as part of a harmonious temporal vision, in keeping with art.”
——Michele Ciacciofera
Cuneiform Script:
Cuneiform script is one of the earliest writing systems in human history, invented by the Sumerians evolving for a long period from 31st century BC to 1st century AD. It is distinguished by its wedge-shaped marks on clay tablets, made by means of a blunt reed for a stylus.
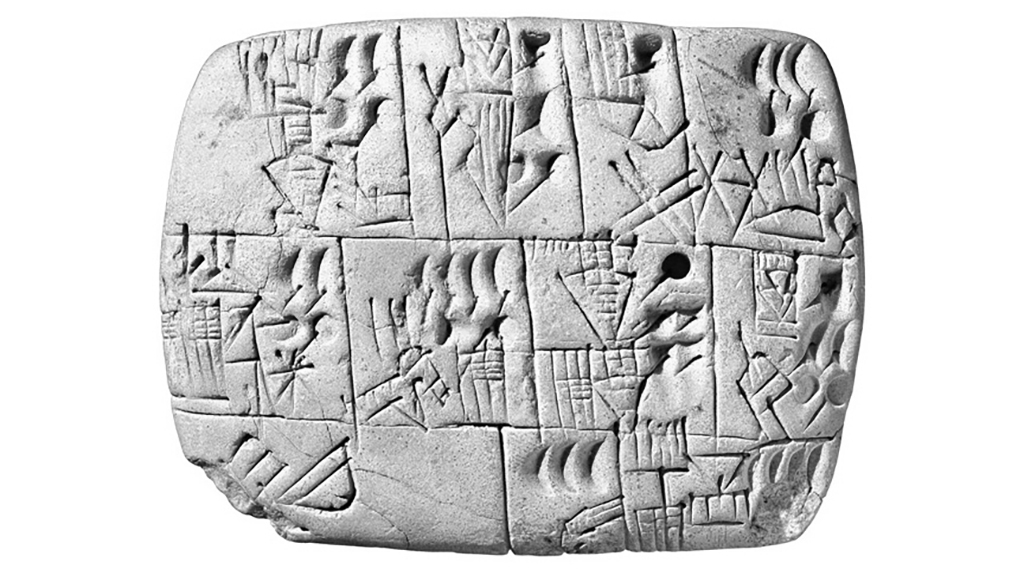

The origin of cuneiform script is tokens used for accounting, a kind of ceramics dingus molded in various shapes. The tokens were preserved in a hollow-ball shape clay envelope with impressing marks on the envelope surface for distinguishing the deposit inside. It gradually developed into abstract marks on clay tablets written by a stylus.
A speculation of the first time cuneiform script given abstract meanings other than accounting is the inscription of names of both gods and human in burial use.
Coptic Script:
Coptic script is the latest stage of the Egyptian language, spoken in Egypt until at least the 17th century as official language. It was gradually replaced by Arabic and eventually became extinct. Coptic script is one of the earliest languages used for the translation of the Bible. One of its distinct dialects, Bohairic, is spoken and written in the Coptic Orthodox Church of Alexandria as the liturgical language nowadays.


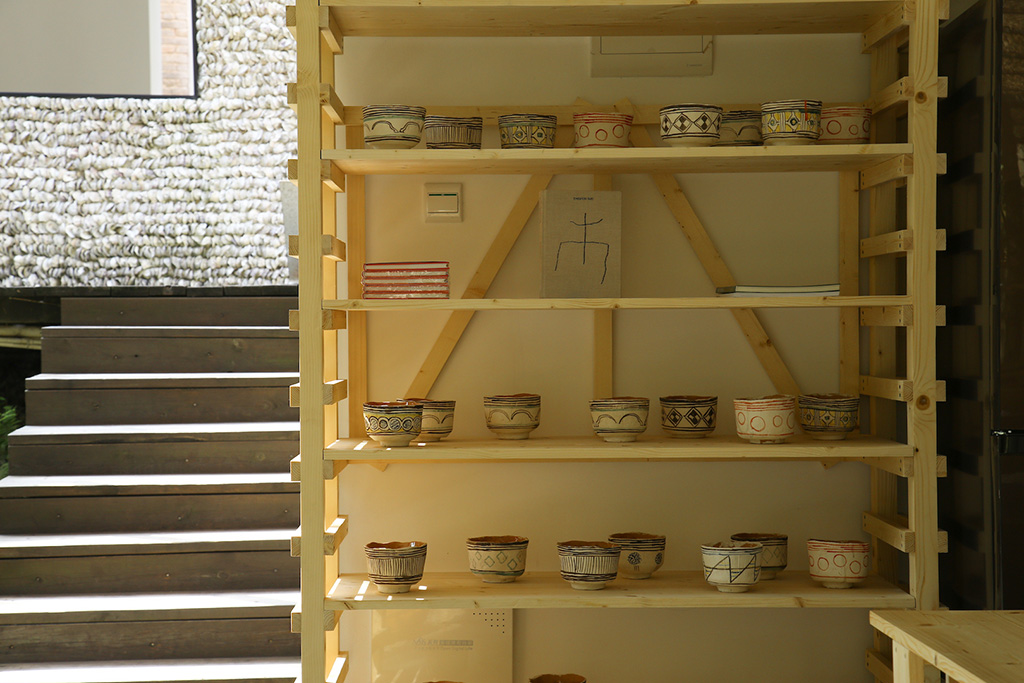
Ceramics / Earthenware
“Producing these works in Sardinia, using mud, clay, straw and the sun of the island was essential for my project, which also has the purpose of underlining the importance I attribute to nature and agriculture…”
“I try to create an image, not a prebuilt image, but an image I search for with ceramic and also raw clay. The relationship with something material that is almost in our genes, communicates something, especially with the earth. The modeling of clay, the prints left by hands, are perceptible to the viewer and go well beyond the aesthetic created by the object. Here I am talking about a stimulation of the senses.”
——Michele Ciacciofera
Sardinia:
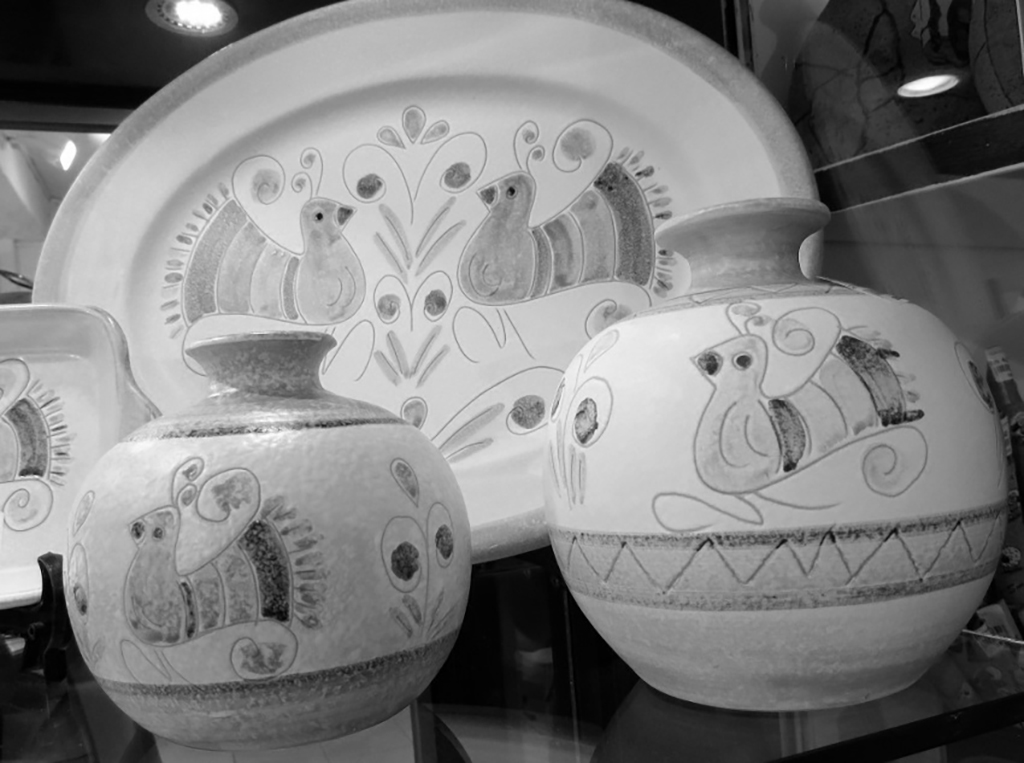
Local history of ceramics production traces back to the Ancient Neolithic period, the first appearance of ceramics (c. 6000-4000 BC) on the island, and continues to contribute in the following cultures, such as the Beaker culture (2100-1800 BC) and Bonnanaro culture (1800-1500 BC). The earliest pottery was not only used in daily practice, but also served as ritual offering container.
Traditional ceramics of Sardinia are mainly terracotta. Each town on the island owns its distinguish style of ceramics. (picture below: patterns of lapwing, symbolizing fertility of the harvests.)

Sicily:
Also began from the Ancient Neolithic period from c. 6000 BC, Sicilian local production of ceramics has a long history.
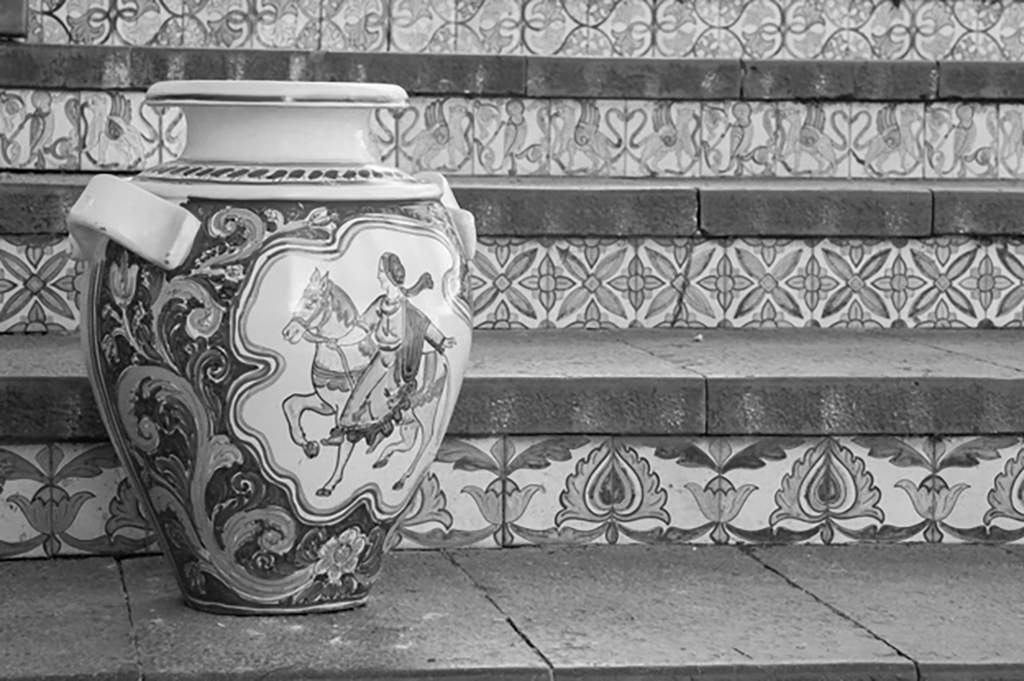
Similarly to Sardinia, Sicily was tinted by various kinds of culture through invasion and immigration for thousands of years. Civilizations, for instance, Arabic, Greek, and Spanish, brought their typical techniques of ceramics to the island, such as maiolica and azulejos:
The maiolica technique was used for all manner of ceramics, from vases to plates to light fittings. It was also used to create azulejos, hard-wearing decorated tiles. As the baroque arrived in Sicily and aristocratic palazzi sprung up all across the island, azulejos were the first choice of flooring. Most were embellished with relatively simple geometric patterns, but the wealthiest members of the nobility commissioned azulejo floors depicting large-scale pastoral scenes, fantastical collections of creatures, family coats of arms and much more. (picture below)

Local ceramics production of both Sardinia and Sicily relates intimately to their natural environments. The clay, water, sun, and colors. All of these originate on these two islands. Furthermore, clay of Sicily contains a unique combination of silicates, which makes the earthenware shines in its unique way.
Indus River Valley Civilization/Harappan Civilization:
The Indus River Valley Civilization, 3300-1300 BCE, also known as the Harappan Civilization, extended from modern-day northeast Afghanistan to Pakistan and northwest India. Important innovations of this civilization include standardized weights and measures, city plan, art making (such as ceramics pottery, seal carving, and metallurgy).
Harappan people used different types of pottery such as glazed, polychrome, incised, perforated and knobbed. There is proof of pottery being constructed in two ways, handmade and wheel-made. Moreover, the glazed Harappan pottery is the earliest example of its kind in the ancient world. Geometrical patterns, circles, squares and triangles and figures of animals, birds, snakes or fish are frequent motifs found in Harappan pottery. Another favorite motive was tree pattern, and sometimes, graphical scenes of Harappan people’s daily lives.
![[ceramics]indus-bowl](http://www.vitamincreativespace.com/en/wp-content/uploads/2018/12/ceramicsindus-bowl.jpg)

Architecture / Engraving
“When I lived in Sardinia, I often went out looking for inscriptions on stones, ancient symbolic writings. I have always tried to bring these symbols back up to date. I have memorized this sort of abstract graffiti, which has only been partially deciphered, in order to find its meaning. I associate it with everyday things.”
“I memorized the engravings on the stones so as to reinvent them or bring them up to date… For me, memory is a mosaic that allows us to manipulate time, going beyond the limits of mankind. Man’s greatest limit is death and so I seek to go beyond this.”
——Michele Ciacciofera
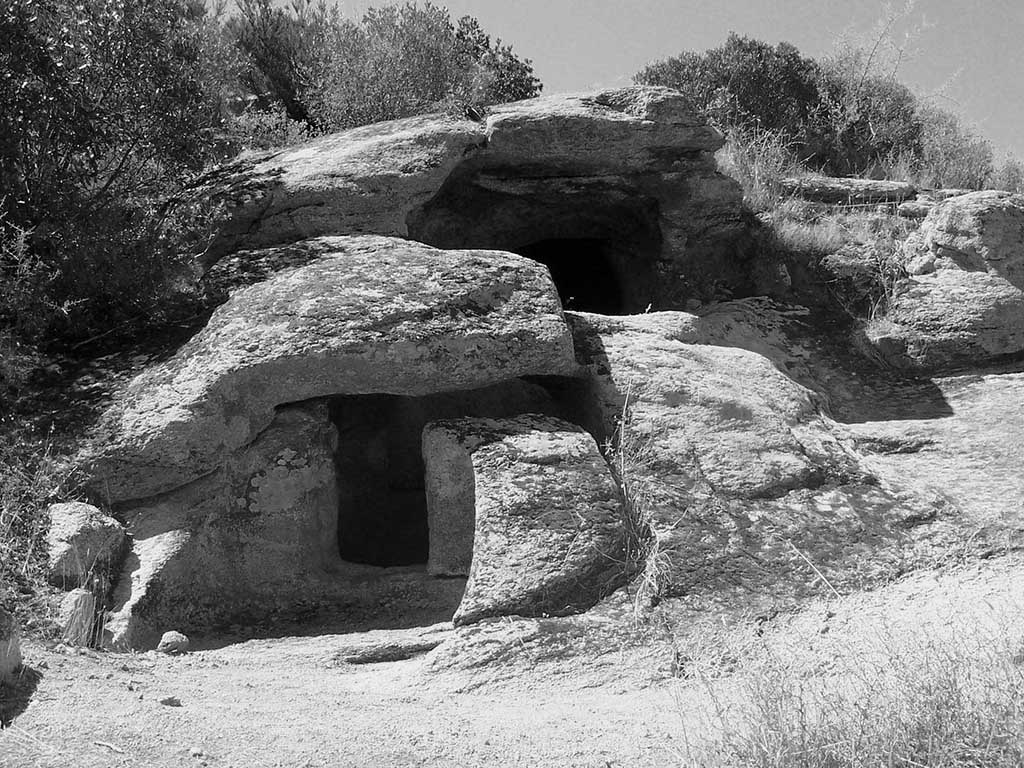
Domus de janas:
“Domus de janas” means “houses of fairies or witches,” a kind of rock-cut underground tombs, built through the Late Neolithic and Copper Age period on the island of Sardinia, also known as the “pre-nuragic” period (built mostly between 3400-2700 BC). More than 3500 of domus de janas still stand widespread on the island.
They have been used in the following civilizations as burial, dwelling, and other purposes. These days, domus de janas becomes one of the most famous tourist spots of Sardinia.

The inner construction of domus de janas mimics the one of dwellings of those days, with a typical sequence: dromos + antechamber + chamber + cells.
Most of the domus de janas were constructed with a single combination of “dromos + antechamber + chamber”, while the quantity and shape of cells is irregular.
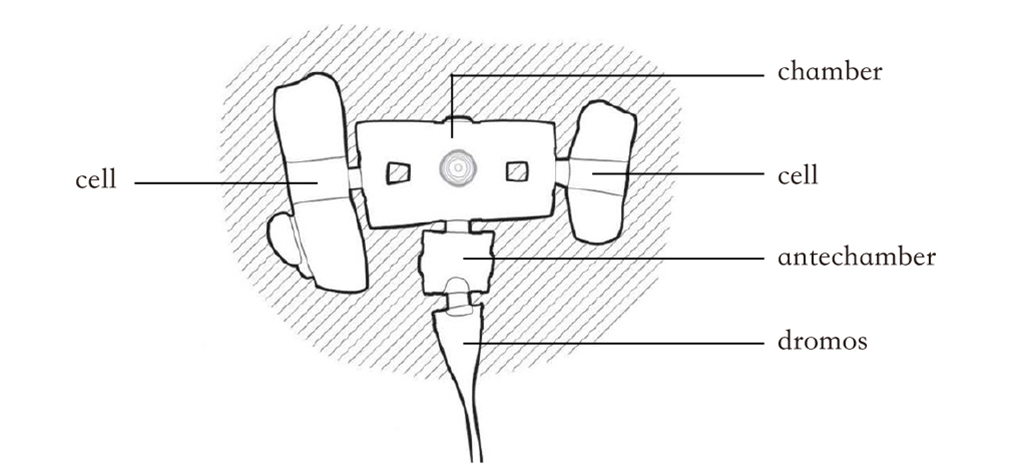
On top of the space structure, there are also unpractical art, such as pillars, columns, wood beams, and hearths, simulating a house for daily living.
There are various sculpted and painted symbols on the wall of domus de janas, such as bucrania (bull-head like form), zigzag, and spiral. All of them remain undecoded.
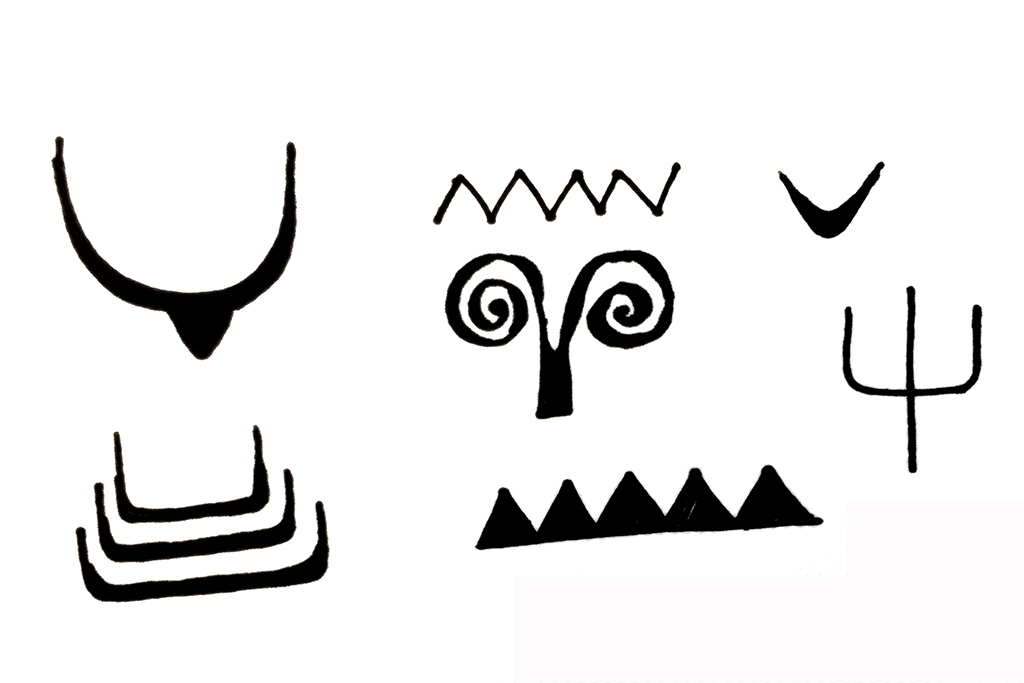
The “false door”, or “imaginary door”, is an outstanding sculpted symbol of domus de janas. A false door is a pattern cut out on the wall with a form imitating a door. False doors usually appear on the back wall of chamber, and on the end of the mutual line composed by the “dromos + antechamber + chamber” structure.
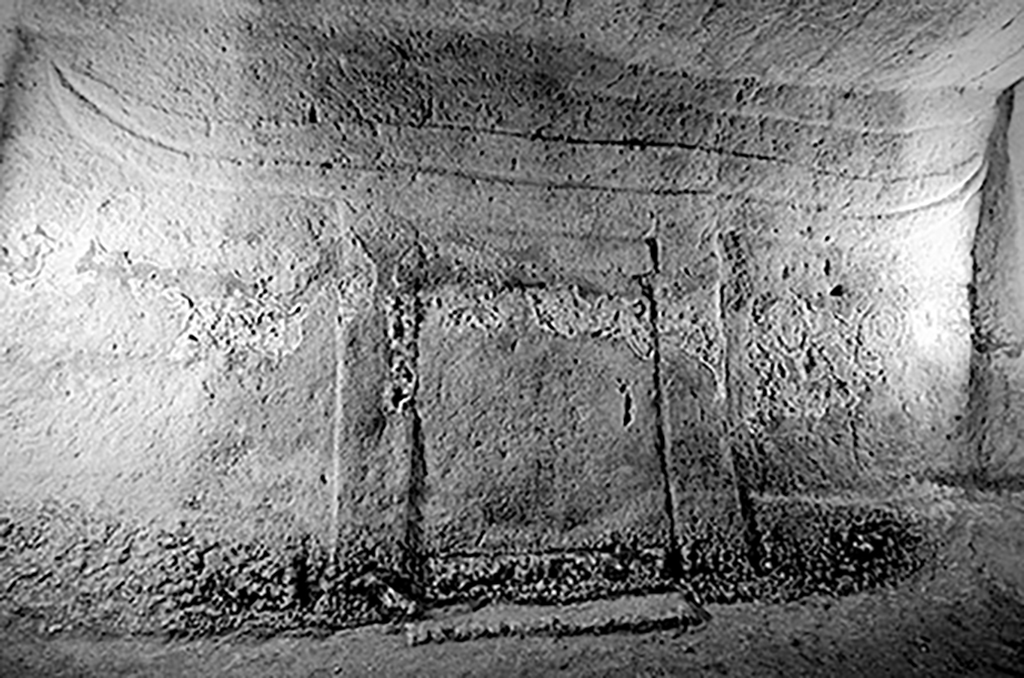

Scholars consider that the false doorway plays a ritual role of transporting the deceased from the society of the living to the one of dead, since it only owns the form of a door while without the practical function.
The linear arrangement of spaces along a mutual axis is emphasized by the alignment of the doorways and other architectural motifs, such as the hearth. The ritual held inside domus de janas is considered to be a gradual process of social transition for the dead, starting at the aboveground end of the dromos, successively through the antechamber and chamber, fulfilling at the false doorway

Culinary
“He (Giovanni Antonio Sulas) told me that one shouldn’t develop only one sense in artistic practice, but several at the same time and that cooking was a vehicle, a means at the heart of my artistic research.”
“The culinary is one of the original grounds of research, practice and experimentation of my artistic activity. I look for the obvious sensations like flavors and scents, as well as a more nuanced sensational palette – the sounds that characterize cooking foods, the vibrant colors, the periods of waiting during the preparation, and also that of the changing seasons, that serve to offer a new array of fresh raw material.”
——Michele Ciacciofera
Sardinia:
Highlighted local products: wine, cheese, sea food, various kinds of food made from wheat (pasta, bread…).
Sicily:
Highlighted local products: wine, olive, orange, tuna fish, various kinds of food made from wheat (pasta, bread…).
Textile
Sardinia:
Before 1960s, all of the girls born and raised in the island of Sardinia must learn to weave and produce a future dowry (corredo) for their own. When a girl married, the corredo would be paraded down the street, held aloft by relatives in a celebratory procession marking the girl’s move from her family’s home to her new one.
Common uses of Sardinian weaving: carpet, saddle bag, chest cover, blankets, clothes⋯
Typical technique of Sardinian traditional weaving:
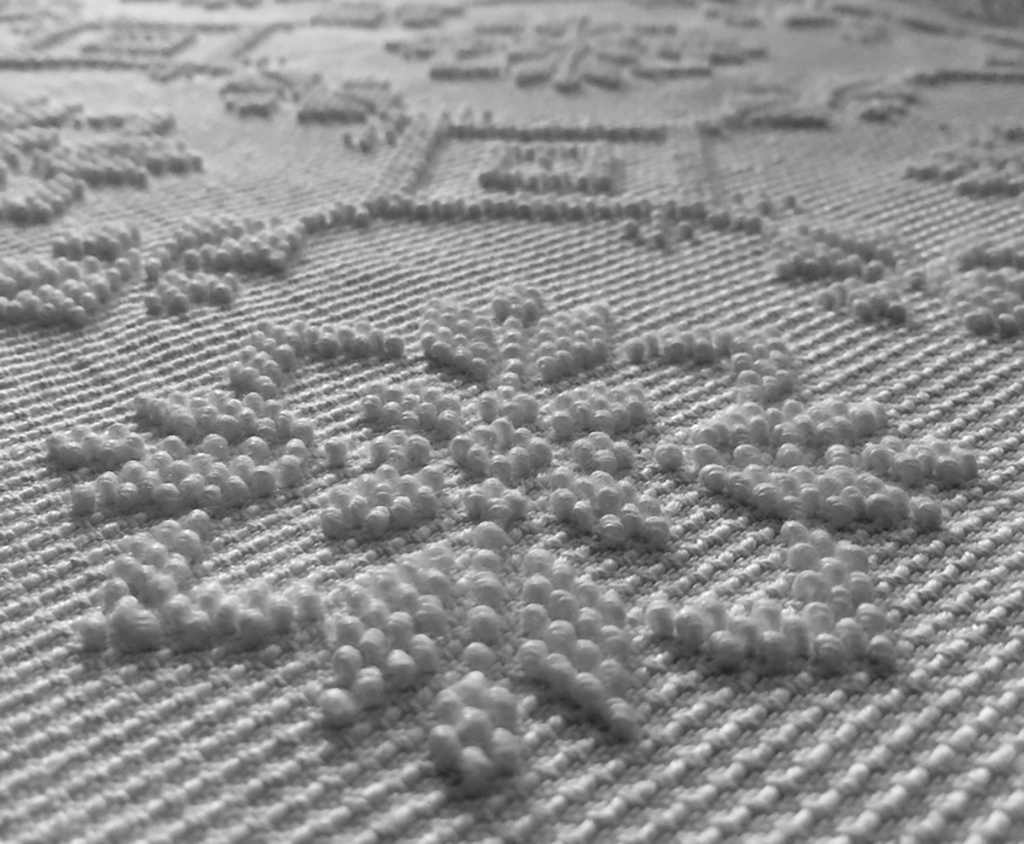
“a pibiones”:A small raised bumps of thread. Each pibione must be counted and wound by hand, one pibione at a time, one row at a time, matched against patterns marked by hand on graph paper.

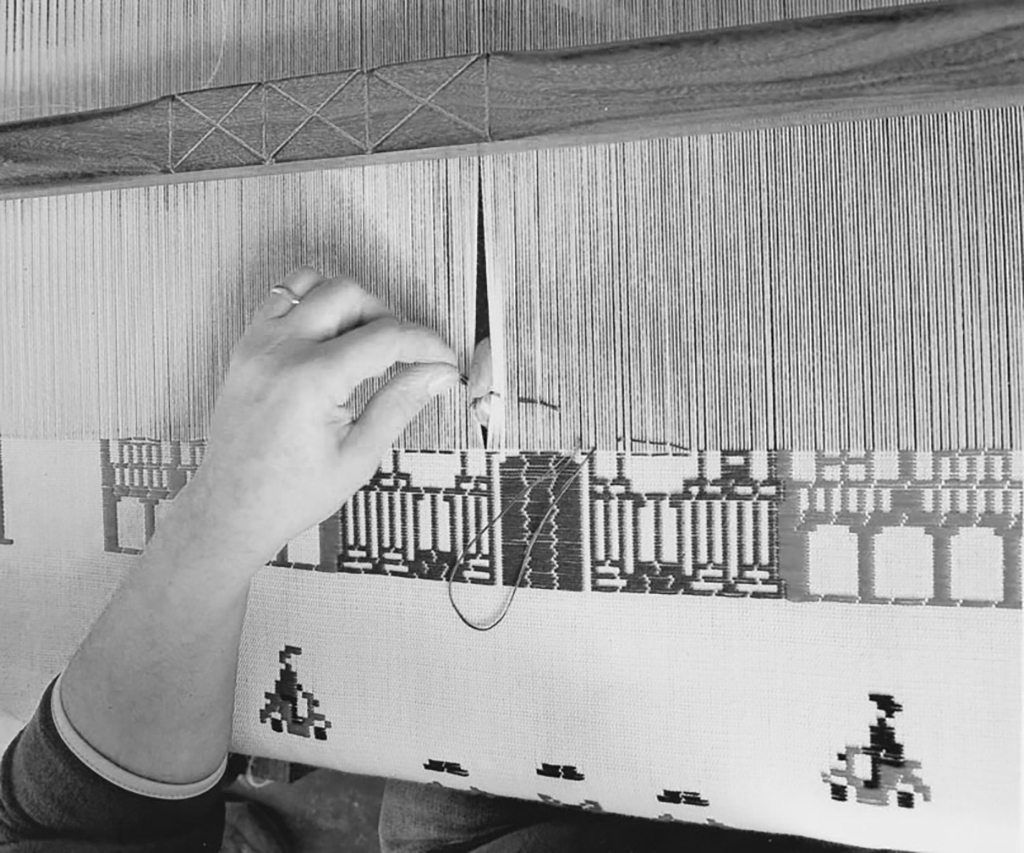
“a bagas”:A bagas means “by fits and starts,” and it is therefore referred to as a weave that includes additional wefts, drawn on the decorative motifs woven on a base tela canvas fabric.
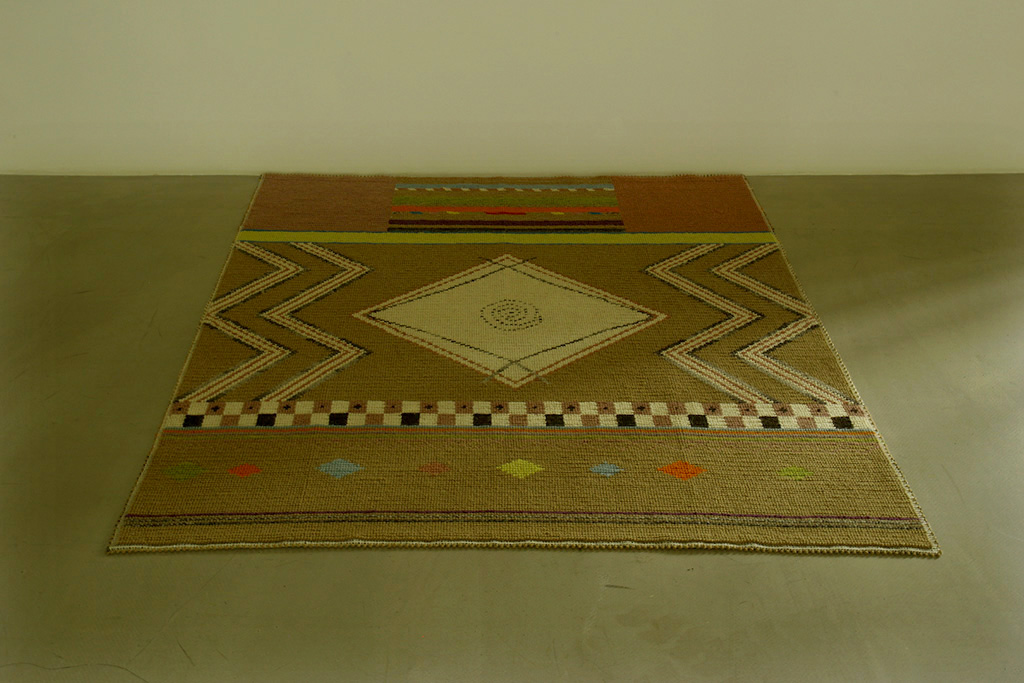


Michele Ciacciofera
Born on the island of Sardinia in 1969 and raised in Sicily, Michele Ciacciofera has always been invested in the relationship between human existence and the natural world. Using a variety of artistic approaches, including sculpture, painting, drawing, theater, video and sound, he freely combines media and methods in his exploration of nature, history, mythology and humanity.
A conceptual artist at heart, Ciacciofera is concerned first and foremost with the subject, narrati
ve and feeling that he wishes to convey, with the materials – drawn from a host of sources – following the concept. He constantly calls upon his background in political science, keen interest in environmentalism, and fixation with individual memory, folding in research, activism, and his own subjective reality to create poetic experiences.
(Edited by Yang Baoyi, All photos about the view at Mirrored Gardens: Wen Peng, Courtesy of Mirrored Gardens Archive)
- – -
A Letter to a Traveller
Dear friends,
How are you doing? Hope everything is going well with you! At the transition of seasons, the “Mirror Gardens” has also experienced the changes of light, plants and space. While new “topographies” and “writings” are slowly emerging, we warmly invite you to come and wander at the Mirror Gardens in the daily opening time. We hope you all will pass through and feel the multitude of parallel worlds in various pace and from different perspectives. Let the dance of thoughts and the wandering of the body converge, and freely discover a space that belongs to you:
Zheng Guogu: Visionary World in a Changing State of Mind
Yangjiang Group: A Piece of Kuang Cao Bright Moon
“Borrowed Scenery” of Danh Vo:
Enzo Mari:1974’s autoprogettazione
Isamu Noguchi: Akari series
Dong pavilion
the shop 2018 edition No.3:
Michele Ciacciofera: The Translucent Skin of The Present
Wish you a bright and beautiful autumn, and hope to have you re-visit again in the daily process.
Mirror Gardens
Daily Opening Time:
11:00 – 17:00, Wednesday to Sunday
Closed on Mondays, Tuesdays
Address: Mirrored Gardens, Si Hai Ma Shu, Hualong Agriculture Grand View Garden (化龙农业大观园,四海马术), Panyu District, Guangzhou
Tel: 020-31043759
Email: mail@mirroredgardens.art
- Mirrored Gardens, Photo: Wen Peng, Courtesy of Mirrored Gardens Archive
- Mirrored Gardens, Photo: Wen Peng, Courtesy of Mirrored Gardens Archive
- Mirrored Gardens, Photo: Wen Peng, Courtesy of Mirrored Gardens Archive
- Mirrored Gardens, Photo: Wen Peng, Courtesy of Mirrored Gardens Archive
- Mirrored Gardens, Photo: Wen Peng, Courtesy of Mirrored Gardens Archive
- Mirrored Gardens, Photo: Wen Peng, Courtesy of Mirrored Gardens Archive
- Mirrored Gardens, Photo: Wen Peng, Courtesy of Mirrored Gardens Archive
- Mirrored Gardens, Photo: Wen Peng, Courtesy of Mirrored Gardens Archive
- Mirrored Gardens, Photo: Wen Peng, Courtesy of Mirrored Gardens Archive
- Mirrored Gardens, Photo: Wen Peng, Courtesy of Mirrored Gardens Archive
- Mirrored Gardens, Photo: Wen Peng, Courtesy of Mirrored Gardens ArchiveMirrored Gardens, Photo: Wen Peng, Courtesy of Mirrored Gardens Archive
- Mirrored Gardens, Photo: Wen Peng, Courtesy of Mirrored Gardens Archive
- Mirrored Gardens, Photo: Wen Peng, Courtesy of Mirrored Gardens Archive
- Mirrored Gardens, Photo: Wen Peng, Courtesy of Mirrored Gardens Archive
- Mirrored Gardens, Photo: Wen Peng, Courtesy of Mirrored Gardens Archive
- Mirrored Gardens, Photo: Wen Peng, Courtesy of Mirrored Gardens Archive
- Mirrored Gardens, Photo: Wen Peng, Courtesy of Mirrored Gardens Archive
- Mirrored Gardens, Photo: Wen Peng, Courtesy of Mirrored Gardens Archive
- Mirrored Gardens, Photo: Wen Peng, Courtesy of Mirrored Gardens Archive






















